WHAT ARE FRP COMPOSITES?
Composites are broadly known as reinforced plastics. Specifically, fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites are comprised of a reinforcing fiber in a polymer matrix. Most commonly, the reinforcing fiber is fiberglass, although high strength fibers such as aramid and carbon are used in advanced applications.
A specific definition of FRP composites for our purposes is: “A combination of fiber-reinforcement and a polymer matrix.” For example, polyester resin is the matrix and glass fiber is the reinforcement. The glass fiber provides strength and stiffness, and the resin provides shape and protects the fibers.
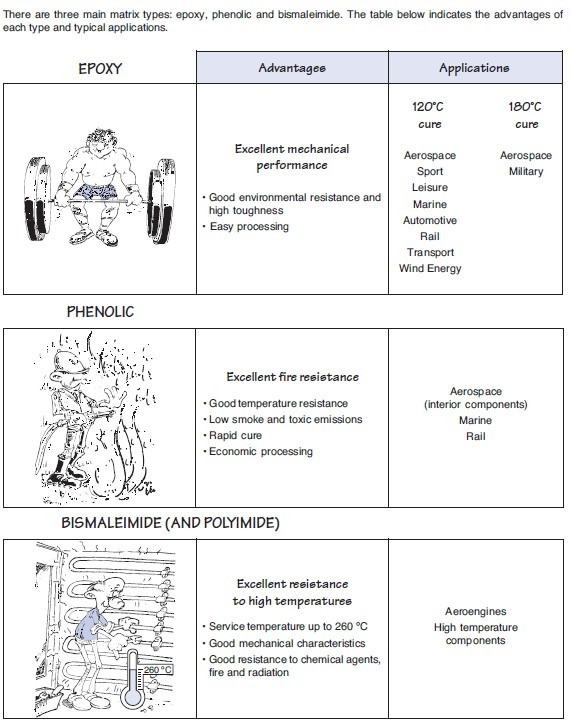
The polymer matrix is a thermoset resin with polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy resins most often being the matrix of choice. Specialized resins, such as phenolic, polyurethane and silicone, are used for specific applications.
Composites typically use thermoset resins, which begin as liquid polymers and are converted to solids during the molding process. This process, known as crosslinking, is irreversible. Because of this, these polymers are known as thermosets and cannot be melted and reshaped.
Common household plastics such as polyethylene, acrylic, nylon, and polystyrene are known as thermoplastics. These materials may be heated and formed and can be re-heated and returned to the liquid state.